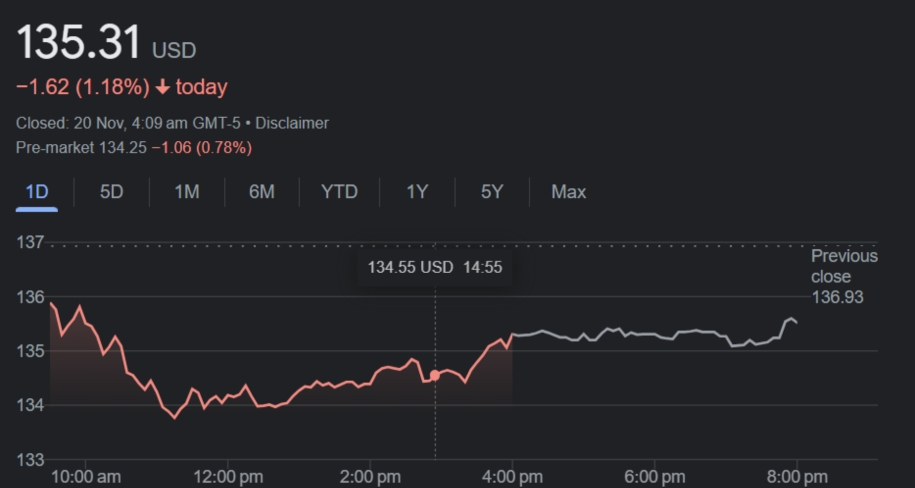
You may be wondering how Google’s stock has performed over the years and whether it’s split at all. As one of the world’s largest tech companies, Google’s stock performance is closely watched. If you’re considering investing in Google or are just curious about the company’s history, understanding the Google stock split timeline is important. Google has actually split its stock twice since going public back in 2004.
While stock splits don’t change a company’s market value, they do make shares more affordable and accessible for individual investors. For every share of Google stock you own, you used to have 14 shares after the splits. Not too shabby! Read on to learn exactly how many times Google’s stock has split, the dates of the splits, and how they impacted Google’s share price.
A Brief History of Google and Its Stock
Google’s initial public offering in 2004 made history. At the time, the search engine company set a record for the largest technology IPO in history. Since then, Google stock has split three times to make shares more affordable and accessible to investors.
In April 2012, Google enacted a 2-for-1 stock split. That means if you owned 1 share of Google stock at the time, you received an additional share. So if you had 10 shares, you ended up with 20 shares. The split essentially cut Google’s stock price in half, making it more attractive for investors to buy in.
Google stock split again in March 2014, this time 3-for-1. If you had 30 shares of Google stock, you received an additional 60 shares. The split tripled your shares and divided the stock price by three.
Most recently, in July 2015, Google (now Alphabet) split its stock 2-for-1 again. If you held onto those 90 shares from the previous split, you ended up with 180 shares after the split.
With more affordable share prices after each split, Google stock became available to more investors. The lower price points gave many people the opportunity to buy into one of the world’s most valuable and fastest-growing companies.
Overall, if you had purchased 10 shares at Google’s IPO price of $85 per share in 2004 and held onto them, you would have 40 shares worth over $12,000 today thanks to Google’s stock split history. Not a bad return on investment! The power of stock splits and a meteoric rise in Google’s share price over the years allowed early investors to build wealth over time.
Google’s IPO and Initial Stock Price in 2004
Google went public on August 19, 2004, at a price of $85 per share. At the time, shares were in high demand and the IPO raised over $1.2 billion, making it one of the largest tech IPOs in history.
Early Growth
On the first day of trading, Google’s stock price rose 18% to close at $100.34, giving the company a market cap of over $23 billion. Over the next 6 years, Google’s stock price rose over 700% as the company’s dominance in search and online advertising grew.
By 2010, Google’s stock price had risen to over $600 per share, making it too expensive for most retail investors. To make the stock more accessible, Google completed a 2-for-1 stock split on April 1, 2014. After the split, investors who held 1 share worth $600 would own 2 shares worth $300 each.
Continued Success
Even after the split, Google’s stock price continued to rise due to the company’s innovative products like Google Maps, YouTube, and the Android mobile operating system. Strong growth and over $100 billion in annual revenue led to a second 2-for-1 stock split on July 15, 2015.
Today, Google’s stock price is over $2,500 per share, giving the company a market cap of $1.5 trillion. For investors who have held Google stock since the IPO, shares have risen over 29,000% and early investors have been massively rewarded. While future stock splits are always possible, for now, owning a single share of Google remains out of reach for most individual investors. But as Google’s track record shows, being patient and holding for the long run can really pay off.
First Google Stock Split in 2014 – The 2-for-1 Stock Split

Google’s first stock split occurred on April 2, 2014. If you owned Google shares before this date, your number of shares doubled and the stock price was cut in half. For example, if you owned 10 shares at $1,000 each ($10,000 total investment), after the split you owned 20 shares at $500 each ($10,000 total investment).
While a Google stock split does not change the actual value of your investment, it does make the shares more affordable to smaller investors and often leads to increased demand and a higher stock price over time. The 2-for-1 split in 2014 meant each shareholder received two shares of stock for every share they already owned.
Making Google Stock Accessible to Investors and Employees
The Google stock split was intended to make Google’s high-priced stock more accessible to smaller investors and employees. At the time, Google’s stock price had risen over 50% in the previous year and was trading around $1,100 per share. The split brought the price down to around $550 per share, allowing more investors and employees to purchase the stock.
Within a year of the Google stock split, its stock price rose over 30% as more investors gained access and demand increased. The split proved successful for shareholders and for Google, demonstrating how a lower stock price and more accessible shares can benefit both parties.
If you were a Google shareholder before April 2014, the 2-for-1 split meant your investment doubled in size overnight. And if you held onto your shares, you benefited from the significant price appreciation over the following months and years. While stock splits themselves do not raise the value of your investment, they often precede strong growth periods and end up substantially raising your investment’s value in the long run.
For Google investors, the first stock split in April 2014 marked the beginning of a very rewarding couple of years. And it represented an important step in Google’s growth from a high-priced tech stock to a mainstream investment holding in portfolios around the world.
Second Google Stock Split in 2015 – The Stock Split in the Form of a Stock Dividend
Google’s second stock split occurred on April 2, 2015. This was a 2-for-1 stock split, meaning each share of GOOGL stock was split into two shares. If you owned one share of Google stock prior to the split, you received two shares after the split at half the stock price.
For example, if you bought a single share of Google for $500 before the split, you would own two shares worth $250 each after the split, for a total value of $500. Stock splits do not change the total value of your investment, they just increase the number of shares and decrease the share price.
The main benefit of stock splits for shareholders is increased liquidity. At lower stock prices, more investors can afford to buy shares, increasing demand and trading volume. This in turn can help support and stabilize the stock price over the long run.
Google’s stock split in 2015 was in the form of a stock dividend. This meant that in addition to splitting each share into two shares, Google issued additional shares to shareholders as a dividend. So if you owned one share before the split, you received two shares after the split and an additional share as a stock dividend, for a total of three shares.
The 2-for-1 stock split and stock dividend effectively cut Google’s stock price in half, making the shares more accessible and affordable to a wider range of investors. Since the split, GOOGL shares have gone on an incredible run, gaining over 250% in value as of early 2021.
Holding Google shares long-term benefited from the stock split and stock dividend. Buying Google stock now comes at a more reasonable price due to the 2015 split.
What Is a Reverse Stock Split?
A reverse stock split is when a company reduces the number of shares outstanding and increases the share price. This is the opposite of a regular stock split, where a company increases the number of shares outstanding and decreases the share price.
Why would a company do a reverse split? Usually, it’s because the company’s stock price has fallen so low that it’s in danger of being delisted from an exchange. For example, NASDAQ requires companies to maintain a share price of at least $1. If a stock drops below $1, NASDAQ may issue a delisting notice. A reverse split is often used to boost the share price back above the minimum.
How It Works
In a basic 1-for-2 reverse split, you would receive 1 share for every 2 shares you currently own. Your total number of shares is cut in half, but the share price doubles. So if you had 2,000 shares at $0.50 before the split, you’d have 1,000 shares at $1 after the split. Your total investment value stays the same at $1,000.
The most common reverse split ratios are 1-for-2, 1-for-5, and 1-for-10, but companies can choose any ratio. The share price is multiplied by the split ratio. So a 1-for-10 reverse split on a $0.20 stock would result in a new share price of $2.
While reverse splits are often necessary for companies to maintain their exchange listing, they are usually seen as a negative event by investors. It often means the company’s stock has been struggling, and there is no guarantee the higher share price will last. However, some companies do eventually recover and go on to prosperity after a reverse split.
In summary, a reverse stock split reduces the number of shares and increases the price. Companies use it to lift share prices, but investors often see it negatively, as it doesn’t alter the market value.
Will Google Stock Split Again? What Investors Need to Know
Google has a history of stock splits to keep its share price accessible to more investors. Given their continued growth and stock price appreciation, will they split again? As an investor, here are some things to consider:
The last Google stock split was in April 2014. They executed a 2-for-1 split, meaning if you owned 1 share priced at $600, after the split you owned 2 shares priced at $300 each. The total value stayed the same but more investors could buy in at the lower price.

- Prior to that, Google split 2-for-1 in 2012 and 3-for-1 in 2006. So they have a pattern of splitting to halve or third their stock price roughly every 2-4 years as the share price rises.
- As of early 2021, Google’s stock price is over $2,000 per share. For many retail investors, this puts the stock out of reach. A split would make the shares more accessible and affordable to buy.
- However, stock splits do not change the company’s market capitalization or value. They are purely cosmetic. While they may temporarily increase demand from retail investors, institutional investors are indifferent.
- Google’s board will consider the pros and cons of another split and make a decision based on what they believe is in the best long-term interests of the company and shareholders. There is no set formula or trigger point for when they have to split.
- If Google does announce another stock split, it would likely take effect 3 to 6 months after the announcement to allow time for all shareholders and brokerages to adjust to the new share count and price.
Google Stock Split: Investor Guidance
As an investor, don’t buy or sell Google stock just based on the possibility of a future split. Focus on the company’s fundamentals and growth opportunities. If a split does happen, enjoy your “free” shares and the potentially short-term bump in demand, but remember it does not change Google’s intrinsic value. The share price could go back up over time, so think long-term!
Conclusion
So there you have it, the full history of Google’s stock splits over the years. While stock splits themselves don’t change the value of your investment, they do make shares more accessible and affordable for individual investors. If you believe in Google and want to invest for the long haul, stock splits are actually good news. Even though Google’s growth has slowed in recent years, its products and services have become deeply ingrained in our lives.
As long as Google stock split keeps innovating and pushing technology forward, its stock should continue to reward patient investors. Of course, there are no guarantees in the stock market. But if the last 20+ years have taught us anything, it’s that you should never bet against Google.
FAQs
Did Google's stock splits affect the company's financial performance?
Google's financial performance wasn't directly influenced by stock splits. However, the moves were strategic, reflecting the company's adaptability to market dynamics.
How did the Alphabetic Restructuring impact Google's stock dynamics?
The Alphabetic Restructuring simplified Google's corporate structure, enhancing transparency. It aimed to reflect the diverse range of businesses under the parent company, Alphabet.
Can investors expect future stock splits from Google?
While future stock splits depend on various factors, Google's history suggests an adaptive approach. Investors should monitor market conditions and the company's financial strategies.
Were there any negative consequences for investors during the stock splits?
While stock splits are generally positive, some investors may perceive them differently. The dilution of ownership could be seen as a potential drawback, impacting certain shareholder metrics.
See Also: How to Make Money on Cash App Without Spending a Dime










